What Are Rats?
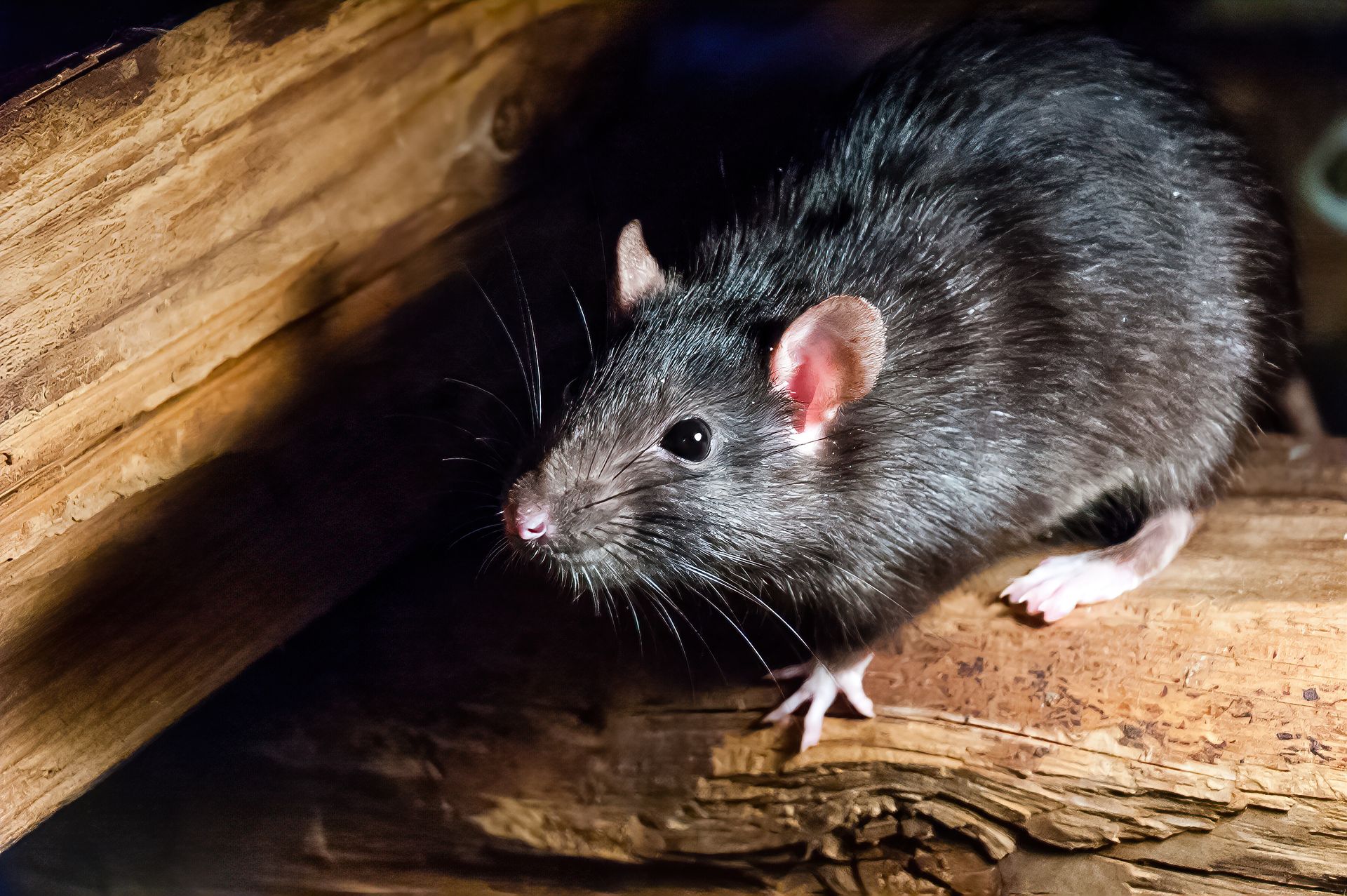
Rats are a small rodent that is closely related to mice and squirrels. They are extremely adaptive and are found all over the world where resources are available. This means that anywhere humans are, there are rats around that thrive off of our trash. They are a common household pest that introduces several problems including disease, property damage, and parasites. They are sometimes domesticated as pets but rats are still generally known as vermin.
Rats Classification & Appearance
Rats are classified under the mammalian order called Rodentia and in the genus Rattus. These rodents are similar to mice but are differentiated by their size and certain features. Rats are larger than mice and typically have long hairless tails to help identify them. Rats’ head are squarer than that of mice who have a pointed snout. Rats also have smaller laid-back ears relative to their head and large front teeth that never stop growing. It is important to note that while rats are identified in name by their color, their actual coat may be black, brown, gray, red, white, and even spotted with 2 or more colors.
Different Rat Species
There are over 50 known species of rats found around the world but the 2 species of “true” rats most common to California are the Norway Rat and the Roof Rat. There are also several species of rodents that are not technically rats that are called rats. These rats include pack rats, kangaroo rats, and bandicoot rats which are all Murine rodents but are not classified under the genus Rattus.
List of Services
-
Norway Rats (Rattus Norvegicus)Item Link List Item 1
Norway Rats are also commonly known as sewer rats. They are strong brown rats that are aggressive and can adapt to severe environments including cold and wet. At maturity, their head and bodies will measure between 6 – 11 inches and can weigh up to 16 ounces. They also have hairless tails that measure an additional 5 – 9 inches long. Their coat is made up of scruffy course hair that is usually brown or gray with a lighter color underbelly. They are typically found close to the ground and prefer to live in burrows, basements, and sewers.
-
Roof Rats (Rattus Rattus)Item Link List Item 2
Roof Rats are slightly smaller than Norway rats but have a longer tail to make up for it. This tail allows them to be nimble climbers who prefer to spend their time in trees, roofs, and attics. Black rats tend to be found in milder climates. At maturity, their head and bodies will measure between 6 – 7 inches and can weigh up to 8 ounces. They also have hairless tails that measure an additional 6 – 9 inches long. Their coat is also made up of scruffy course hair that is usually black with a lighter color underbelly.
Rat Behavior
Rat Diet
Rats have an insatiable diet that requires them to constantly eat at least a third of its weight every day to maintain healthy function. They are omnivorous animals whose diets are not limited to traditional food items. Rats will also feast on soap, fur, leather, bugs, dog poop, and even other bugs in addition to their normal diet of grains, fruits, veggies, and proteins. Rats will hunt for food if needed but they generally rely on scavenging to supply their diet. They are also smart enough to store food like squirrels and chipmunks to ensure that they can survive leaner periods without the same supply of available resources. In addition to the necessary food to survive, rats also need at least one ounce of water every day. Rats are cautious creatures, so they tend to stay within their territory and don’t really venture too far from their nest for food unless food is scarce.
Rat Reproduction & Lifecycle
If rats are not controlled, rat populations can get out of hand extremely fast. Rats can reach sexual maturity between 5 weeks and 3 months. After that period, rats will have litters every 2 – 3 months with litters ranging from 4 -12 rat pups per litter. Rats are such prolific breeders that a female rat’s gestation period is only 21 days long and they will get pregnant within 48 hours of having her previous litter. This will continue until for about a year until the rat dies. For rats that are domesticated, their lifespans can last for up to 4 years but wild rats living past 2 are almost unheard of.
The number of offspring is largely dependent on the species of rat and the resources available to support a litter of newborn rat pups. Rats may even cannibalize their own young if available resources are lost and the adults can no longer provide for the pups. When resources are scarcer, litters will be cut back to litters in spring through fall when resources are most abundant. Otherwise, when resources are plentiful, rats will continue to breed all year round.
Where Do Rats Nest?
Rats search for 3 things when looking for a nesting site to build their home:
- Warmth: This generally comes with shelter but being protected from the cold and elements helps ensure a healthy litter of rat pups.
- Access to food and water: Rats have to constantly be eating and nourishing themselves and their litter. Rats also prefer to stay within close proximity to their nest so food and water must be accessible close by.
- Access to nest building materials: Rats will need to be able to build their nest using soft materials to create a warm, dry, and comfortable place to rest and raise their young.
Norway rats tend to nest in tunnels or burrows if out in the wild but will settle for basements and sewers when in urban settings. They can also dig under foundations and will take shelter under decks, patios, and in crawlspaces. Norway rats will scavenge soft materials like paper and clothe which will get dragged down into the burrow to create a comfortable nest. Roof rats prefer nesting sites that are higher up in tree branches and will sometimes find their way into your attic. There they will create a nest out of soft building materials like insulation and paper to keep them warm.
Interesting Facts About Rats
- Rats shed over 500,000 hairs a year which make these rodents horrible for allergy sufferers.
- Rats’ front incisors will continue to grow throughout their lives requiring rats to constantly chew to wear them down. Rats can and will chew through just about anything including wood, plastic, aluminum, copper, lead, drywall, concrete, etc. The only thing they don’t chew on are certain hard metals and glass.
- Norway rats are excellent swimmers while roof rats are extremely agile climbers.
- Rats have an extremely strong sense of smell and hearing but horrible eyesight.
- Rats are nocturnal and usually leave the nest at dusk to scavenge for food.
- Rats are cautious creature who avoid contact will all other animals as much as possible.
- Rats are never too far from their nests, and they are creatures of habit, following the same trails to and from their home.
- Rats can be social creatures with territories and colonies. One dominant male usually controls several females and will act aggressively against other males.
- Rats have flexible bones which allow them to navigate their way through extremely small passages.
What Attracts Rats?
Rats are primarily attracted to shelter, food, and water. If a rat can find a place where it is provided those 3 elements, the rat will stick around.
Plants that attract rats:
Roof rats in particular, like to feed on fruits and vegetables that grown from gardens and fruiting trees. Planting these types of plants around your home provides rats with a steady source of food for them to eat. Rats prefer to eat lemons, oranges, peaches, avocados, figs, and nuts like walnuts and almonds. This also means that any fruiting trees need to be cleaned up for any rotting fruit that may have fallen to the ground.
Smells that attract rats:
Rats have an excellent sense of smell and certain smells can either attract or deter rats. The smells that attract rats are those that smell like food. This means that strong odor that come from your trash, barbeques, birdfeeders, gardens, and even pet food that is left outside can all attract rats. Keeping places clean and organized is a great way to remove most of these smells to help minimize rat activity.
Debris and clutter attract rats:
Rats are cautious creatures that prefer to not be exposed. This is why they prefer to take shelter under debris, so they are less visible to predators like cats and birds. Having debris like fire wood, leaf piles, untrimmed bushes, etc. all provide rats with the coverage they like to travel about free from the threat of predators.
Sources of hydration attract rats:
All living things, including rats, need some water to stay hydrated. Removing standing water from pet dishes, bird baths, and fixing leaks and irrigation will help reduce water sources for rats and other rodents.
How Do Rats Get in Your Home?
Rats are extremely smart creatures that have been shown to figure out puzzles and even remember how to trigger certain mechanisms to unlock food. They use this understanding of the world around them to figure out how to reach the source of food or shelter that may be inside your home. While rats are cautious creatures, they can and will find ways to get into uncharted territory. This means that they will either locate an existing pathway or create a new one into your home or business. If they can’t find access, rats will use their teeth to chew through wood, metal, and plastic to reach the inside of your home.
Rats have been known to swim in through the plumbing and into toilets, crawl in through open doors and windows, chewed through drywall, and more to access parts of homes they were not invited into. If they can’t find their way in or chew their way in, they can also climb in. Roof rats are extremely agile climbers who will use tree branches as bridges to access rooftops where they will chew their way in through the roofing materials.
Are Rats a Threat?
Rats are extremely problematic rodents that can cause extensive damages as well as spread disease.
Rat Damages
Rats cause hundreds of millions of dollars in damage to homes and businesses every year. They chew on building materials which causes structural damages and on wire which increases the likelihood of a fire. In addition to destruction of real estate, rats are also known to be extremely destructive to personal property like vehicles, furniture, books, and clothes. Rats are known to infest cars and trucks and destroy the belts and cables necessary for the engine to run and ruin upholstery, books, and clothes for nesting material. Rats will also devastate a garden or commercial agricultural crop causing farmers massive financial problems.
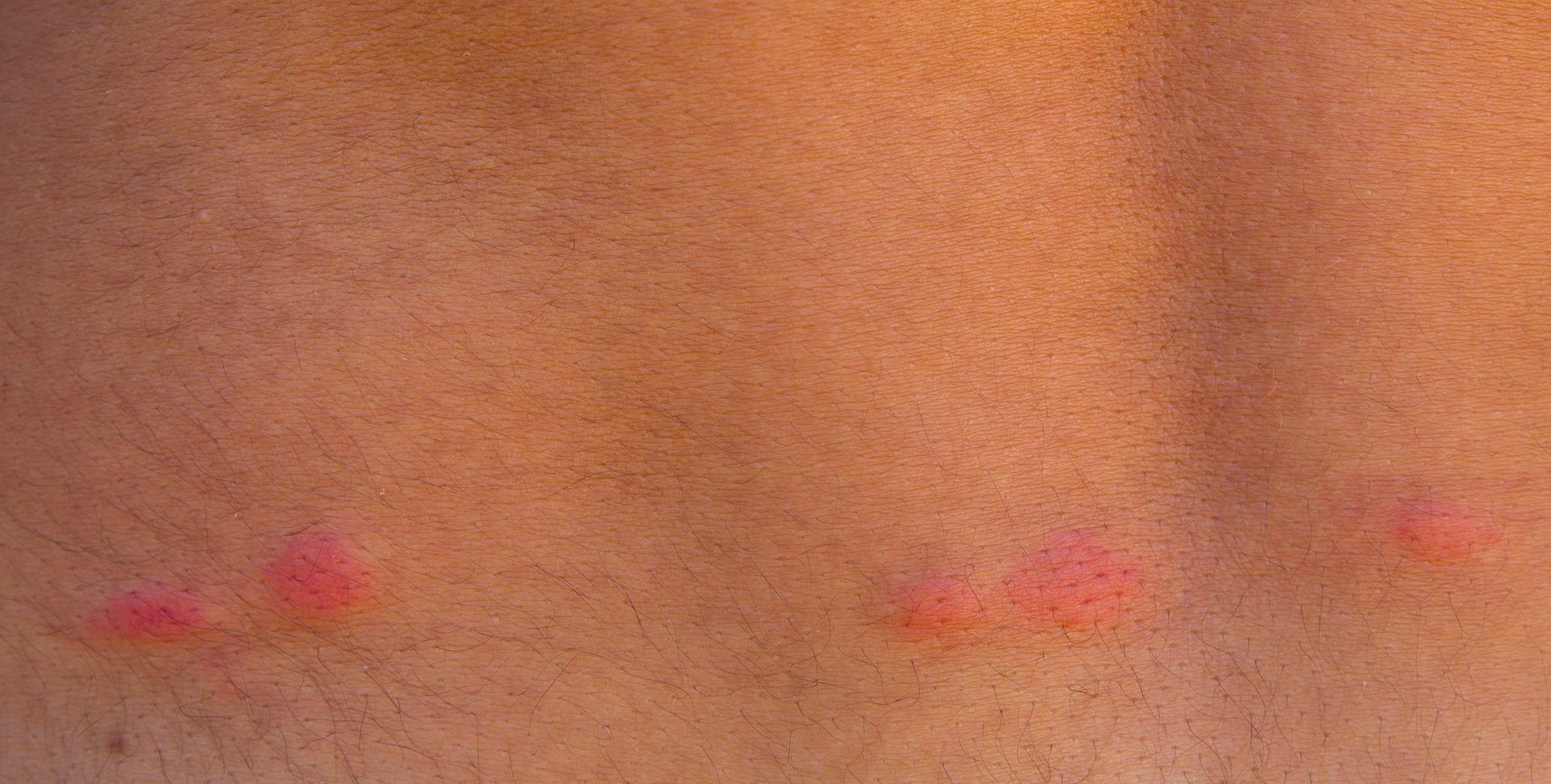
Rat Bites
Rat bites are rare, but they have been known to act aggressive when cornered. If they do bite, there is a chance of infection from diseases like rabies and rat bite fever.
Rat Diseases
Rat diseases can be spread through direct contact, bites, exposure to infected droppings, eating contaminated food or water, and exposure to rat related parasites. These diseases are serious and will generally require treatment to mitigate the symptoms of rat related diseases. The most notorious of the rat diseases is the black death pandemic that hit the dark ages. The spread of the bubonic plague was said to have been caused by fleas that were carriers that were brought into households by rats.
How to Prevent Rats
Rat prevention can be summed up in 3 steps:
- Cleaning / Sanitizing: The most important part of prevention is cleaning up and removing all trash followed up by sanitization. By removing all rat attractants, you minimize a rat’s desire to nest. This generally requires putting away and sealing up all food sources, using bleach to disinfect surfaces, etc.
- Exclusion: After cleanup, exclusion is the next most important part of rat prevention. If access points are sealed, then rats can’t find their way inside. This generally includes installing vent caps, screen mesh over access points, cutting back tree branches, sealing gaps, etc.
- Deterrents: Using rat deterrents should be used with the other 2 prevention strategies as deterrents are the least effective prevention strategy. When used on their own, rat deterrents only work if a rat isn’t desperate for a meal.
Recognizing Signs of a Rat Infestation
There are several signs that are commonly associated with rat activity:
- Rat poop – The dead giveaway of rodent activity is seeing signs of rat poop and droppings around the house. Rat droppings are black and pellet shaped like a grain of rice.
- Rat tracks – Rodent tracks are usually visible when there is a surface of dust that gets disturbed.
- Signs of gnawing – Rats will chew constantly on hard surfaces to try and grind their teeth down. Seeing signs of teeth marks on plastic, wood, concrete, or other building materials can indicate a rat problem.
- Rat burrows – The entrances to these rat burrows is likely the only thing you will see but they can be found along the foundation’s edge or along fences and under vegetation.
- Rat runways – Rats prefer to follow the same path so rats will wear down pathways.
- Grease marks – Rats produce oily fur which leaves unsightly stains along baseboards and hard wood floors.
- Urine stains – Urine will be difficult to see without black lights but the smell of it can become noticeable in large enough quantities.
- Rat nests – Nests will usually be found in areas that are quiet and undisturbed like crawlspaces, wall cavities, attics, and basements. These will be made up of shredded cloth, paper, and other loose soft materials.
- Food with chewed packaging – Food that has disturbed packaging with bite marks and sections gnawed away indicate that the food has been contaminated by a rat or mouse.
- Sound from inside the walls – Rats are nocturnal and will use wall cavities to traverse their territory. This can often be heard at night as what sounds like scratching coming from inside the walls.
- Funky smells – Rats give off a strong musk scent in addition the strong smell of urea that comes from their urine.
How to Get Rid of Rats
Effective rat control basically comes down to trapping and baiting. Rats that have made it inside your home will need to be exterminated and removed using one of the different trap style methods:
- Snap trap: This is the more traditional trap that uses a spring-loaded mechanism and trigger to snap shut on a rat to execute it quickly.
- Glue trap: Glue traps are less humane and catch rats using an incredibly strong adhesive to prevent the rat from moving.
- Live trap: This uses a bait and a cage to trap rats alive to be released or exterminated and removed.
A couple notes about the snap traps that should be remembered are:
- Mouse snap traps will not be effective on rats due to their size.
- Rats are cautious so snap traps are most effective when they are left out unset for a few day so rats become familiar with them as part of their environment.
- Do not place snap traps in the path of children or pets and instead place them where rat activity is visible.
- Peanut butter is a good go to bait that is effective due to its consistency.
Rat baits should only be used when rats are a problem outside because baits don’t kill rats instantly. Instead, baits take several hours to days to work which could cause a rat to return to its nest before it dies. If the rat’s nest is inside your home, the bait will work against your favor and cause the rat to die inside where it will decay and stink up any surrounding areas for a short period.
How to Clean Up After Rats
Cleaning up after rats is extremely dangerous because of the presence of diseases like hantavirus. Hantavirus is spread through exposure to infected urine and droppings. This means that dried rat waste that has become dust particles can be breathed in when agitated during cleaning. This can cause hantavirus and other waste borne pathogens to enter your system, causing an infection.
To ensure that this doesn’t happen, it is recommended that the proper precautions are taken when dealing with rat cleanup. Be sure to wear protective clothing including glasses and a respiratory mask to filter pathogens. Be sure to air out any place that has been exposed to rat waste at least 30 min prior to cleanup to allow infected dust to clear out as much as possible before cleaning.
When to Call a Professional to Help with Rat Control
If you have been dealing with rats or have seen signs of rat activity, call an EcoGuard Pest Management rodent expert to come inspect your property. We will design a custom plan to ensure that rats no longer present a problem for you and your home. Call (866) 326 2847 today to get your rat inspection scheduled.
Rat FAQs
-
Why are rats a problem?
Rats are vectors for disease and are known to carry over 30 diseases that are transmittable to humans. These diseases can cause serious health implications that are difficult and expensive to treat. In addition to health problems, rats are also extremely destructive, and populations can get out of hand in a very short period of time.
-
What kills rat immediately?
The most effective method of rat control utilizes snap traps to exterminate rats. If they are placed properly in areas of high rat activity, snap traps are extremely effective.
-
What are rats afraid of?
Rats can be deterred by anything that irritates their most sensitive senses but the thing they are afraid of is predators. Studies have shown that a rat’s anxiety and stress response intensify in the presence of cats and predatory birds.
Request A Free Estimate
We will get back to you as soon as possible
Please try again later
Immediate Service Available
Services
Customer Care
Legal
Working hours
- Mon - Sun
- -
All Rights Reserved | EcoGuard Pest Management | All Phone Calls Recorded | By Using Website You Agree To Terms Of Use