What Do Cockroaches Eat?

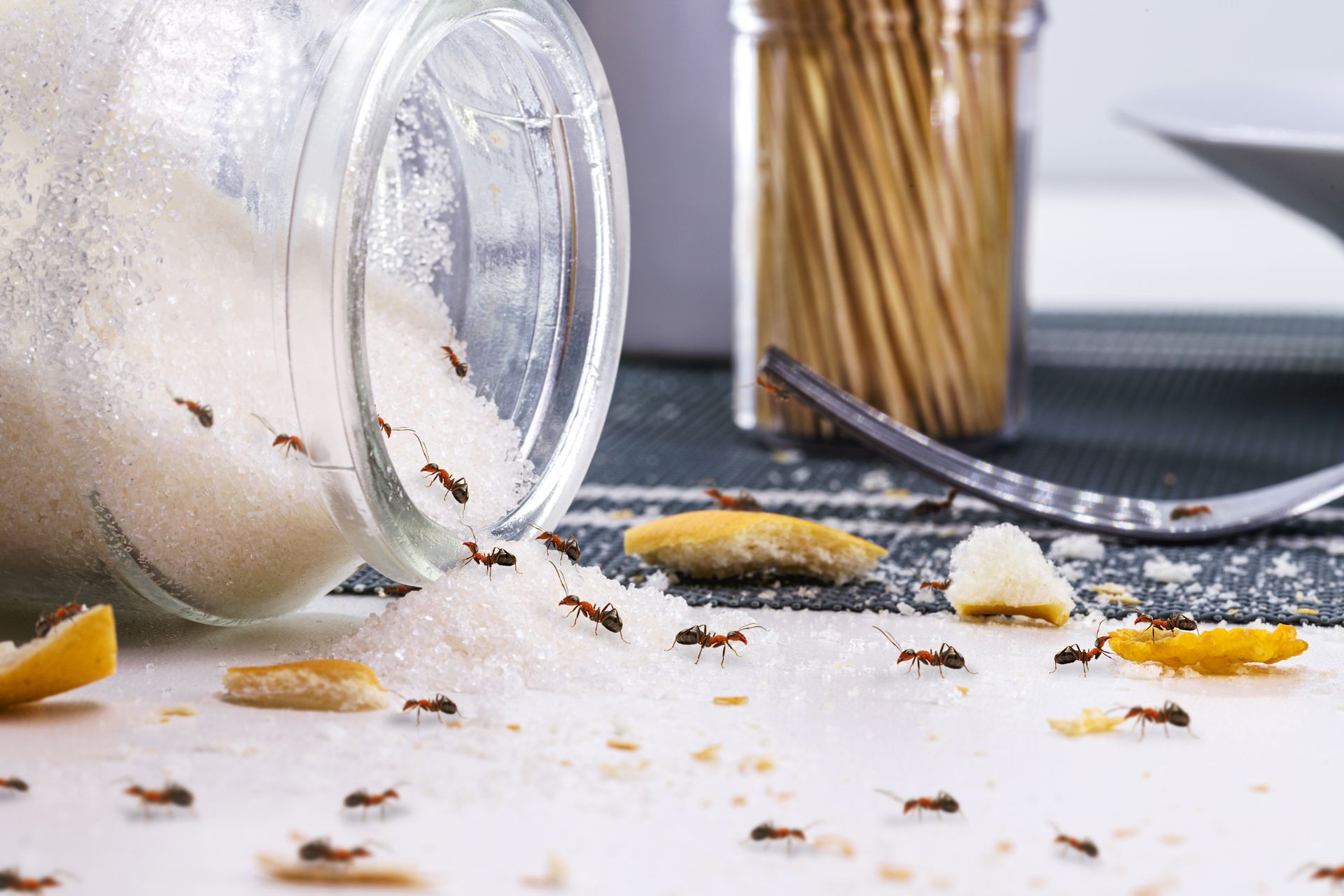
Cockroaches, by nature, are omnivorous and opportunistic eaters. These insects exhibit an extensive dietary range and can consume just about anything organic including plant and animal-based materials in addition to unconventional items like hair, fingernails, soap, toothpaste, book bindings, wallpaper glue, human waste, and even their own cast-off skins. Cockroaches are highly adaptive to the available food in their environment and are one of the least selective eaters in the insect kingdom. Their wide-ranging diet means they can survive even when normal food sources are unavailable.
Understanding the eating habits of cockroaches can play a vital role in pest control efforts. Identifying their preferences can aid in managing infestations effectively, regardless of the specific cockroach species involved. Moreover, since cockroaches also demonstrate a fondness for fermented and decaying materials, this makes them vectors for disease and bacteria. For this reason alone, effective cockroach management is critical to ensure that they do not contaminate human food sources in their search for sustenance.
Cockroach Diet
Cockroaches have an extensive and adaptive diet that is often determined by their immediate environment. Their tastes encompass items commonly consumed by humans as well as other unconventional organic substances. For instance, cockroaches inhabiting sewers may consume sewage, while those found in forests might feed on decaying wood. Within human spaces, they are attracted to a variety of foods, including but not limited to:
- Sweets and starchy foods
- Greasy foods and meats
- Cheese, particularly if it's moldy or fermented
- Decaying organic matter
- Household items such as cardboard, book bindings, wallpaper glue, and even soap and makeup
These pests are also notorious for finding their way into containers that contain items like sugar, flour, chips, and cereal. Cockroaches' feeding preferences are notably human-like, with a particular affinity for junk food-like substances.
Interestingly, in instances where food becomes scarce, they have been known to resort to cannibalism, feeding on their own molted shells and even other cockroaches. In extreme cases, they may even bite humans even though this occurrence is extremely rare. It's also worth noting that different species of cockroaches, such as German and American cockroaches, may exhibit slightly varied dietary preferences.
Their opportunistic nature, coupled with their ability to eat a broad spectrum of materials, makes cockroaches difficult to eradicate but also indicates areas to target for effective pest control. Cleanliness, secure storage of food, and swift disposal of waste and clutter can significantly minimize the presence of these pests.
What Do German Cockroaches Eat?
The German cockroach is a species notorious for its adaptability to indoor environments, particularly within homes. These cockroaches are typically found in areas that are warm, humid, and close to food sources like kitchens, dining rooms, and bathrooms. As nocturnal scavengers, they are known to crawl through these spaces in search of food scraps, demonstrating the ability to penetrate paper and access food not stored in airtight containers.
The German cockroach's diet is extensive and encompasses a variety of items that you may find in a typical household. They have been observed to consume desserts, meats, and fruits, along with more unorthodox foods such as feces and mouse droppings. In particular, they display an attraction to:
- Bread or cereals
- Sugary substances like sugar, soda, or juice
- Various meat products
- Pet’s food
Furthermore, any food products left out overnight are potential targets. Therefore, properly securing these preferred food sources can be a significant step towards controlling a German cockroach infestation.
What Do American Cockroaches Eat?
American Cockroaches, one of the most common cockroach species globally, are notable for their larger size and their ability to fly. Unlike German Cockroaches, they are typically found outdoors in dark, warm, and damp places like sewers or basement drains. However, they can also invade homes, particularly during hot or dry outdoor conditions. Similar to their German counterparts, American Cockroaches are scavengers and exhibit a wide dietary range, including even some quite unconventional food sources.
Outdoor, these roaches consume a variety of items such as:
- Dead or wounded cockroaches
- Small insects
- Decaying leaves
- Fungi
- Wood particles
While indoors, the American cockroach shows a preference for:
- Food crumbs on the floor
- Spilled food in the sinks
- Tea and milk
- Fermented foods like cheese
- Bakery goods
Interestingly, they also show a particular fondness for fermenting or rotting foods, which can often lead them to congregate around garbage cans or compost heaps. Given their wide dietary range and potential to spread disease and contaminate food, it's vital to address any American cockroach infestations promptly.
What Do Wood Roaches Eat?
Wood roaches, contrary to some other cockroach species, primarily have a diet based on decaying organic matter and are not generally drawn to human food sources. This makes them less likely to infest indoor spaces like kitchens. Their diet primarily consists of:
- Dying trees
- Decaying leaves
- Rotting wood
Given their preference for decaying organic materials, environments with ample old wood or leaf piles can potentially attract wood roaches. Therefore, maintaining cleanliness by removing such piles around the house can be an effective preventative measure against wood roach infestations.
What Do Cockroaches Eat if Nothing Else is Around?
Cockroaches possess remarkable adaptability when it comes to their diet, resorting to unconventional food sources if typical ones are unavailable. These insects are capable of consuming a variety of materials that humans would not consider edible, thanks to their ability to digest cellulose amongst other materials. This broad dietary range includes:
- Starchy items such as book bindings, paper, wallpaper paste, and stamp glue
- Protein sources like dead insects, animal skin, and even human hair
- Keratin-based items like calluses, dead skin flakes, and fingernails
- Organic materials like decaying plants, dead wood, waste, and sewage
- In extreme scarcity, they may resort to cannibalism, consuming their own young
However, it's crucial to note that cockroaches usually prefer human food due to its ready availability and higher quantities.
Where Do Cockroaches Find Food?
Cockroaches can source food from various places within the home due to their excellent scavenging abilities. The kitchen is one of the primary areas where cockroaches can find food. They can easily feast on:
- Food left on countertops
- Tiny crumbs in food preparation areas
- Splatters around stove burners
- Stray pieces of food left in the sink
- Unsealed leftovers of food packaging
- Pantry items such as chips, cereals, or sugar
Floors, especially carpets, are also common areas that provide ample food sources for cockroaches as they often collect crumbs. Roaches are usually crawling around on the ground seeking out even the tiniest food particles with their strong sense of smell.
Pet food is another potential source of nourishment for these pests, as its composition is close enough to human food from a cockroach's perspective. Cockroaches are likely to consume leftover pet food, crumbs, or residue that might be left in pet bowls.
To reduce cockroach attraction and infestation, maintaining cleanliness by regularly cleaning countertops, sinks, and floors is crucial. Storing food items, including pet food, in airtight containers can help keep these pests at bay. It's also advisable to regularly clean pet bowls and pick up after pets, as cockroaches are also known to eat feces and other decaying matter.
How Cockroaches Affect Human Food
Cockroaches pose a significant threat to human food, mainly due to their preference for scavenging in unhygienic locations. From sewers to litter boxes, cockroaches can transfer harmful pathogens to our food and cooking surfaces merely by traversing them. This ability can result in various health complications, such as food poisoning, diarrhea, and dysentery, among others.
How Do Cockroaches Eat?
Cockroaches employ their rudimentary mandibulate mouthparts to bite and chew their food. Their mouthparts' structure allows them to break down various materials including thin plastic and paper, a capability not shared by pests like bed bugs or mosquitoes that have piercing and sucking mouthparts. Common city-dwelling species such as the German, Oriental, and American cockroaches can all exhibit this behavior. Hence, during a cockroach infestation, it's advised to store all food items in cockroach-proof containers or inside the refrigerator to prevent access and reduce the appeal of your home to these pests.
How Do Cockroaches Digest What They Eat?
Cockroaches boast a complex digestive system that hosts symbiotic bacteria. These bacteria assist the cockroach by breaking down and metabolizing a wide variety of substances including harmful compounds and cellulose, a component found in plant materials and various man-made objects. The ability to digest cellulose grants cockroaches a dietary advantage and allows them to consume and gain nutrition from organic materials like paper, cardboard, book bindings, and plant debris. This ability is not shared with many other animals and insects outside of termites and a few other insects. This metabolic versatility is largely credited to the cockroach's evolutionary journey spanning millions of years, during which they have adapted to survive in harsh conditions and consume a wide variety of substances. This remarkable dietary resilience has been verified by scientific studies, including one that found a significant part of the American cockroach's genome is dedicated to metabolizing toxic or dangerous materials.
How Long Can a Cockroach Survive Without Food?
Cockroaches are extremely capable of surviving for long periods without food. While their diet is broadly varied, American cockroaches can survive for months without feeding but can only survive around a month without hydration. Similarly, German cockroaches can last about 42 days without food, but they’re only able to endure approximately 12 days without water. Most cockroach species can manage for extended periods without food, but a consistent water supply is crucial for their survival. Without water, their survival timeframe reduces dramatically to just a few days to a couple weeks.
How to Eliminate Cockroach Food Sources
Eliminating cockroach food sources is a key strategy in pest control, as it makes your home unappealing to these insects. Here are some key steps to take:
- Store food properly: Keep all food items in air-tight containers. This includes leftovers and open foods. This reduces the availability of easy food sources for cockroaches.
- Clean your environment: Wipe up spills immediately and maintain a clean kitchen. Regular cleaning, especially in food preparation areas, is critical. This should extend to a regular sweep, mop, and vacuum routine for all floors to remove any potential food particles.
- Manage waste effectively: Empty your garbage on a regular basis and rinse cans, bottles, and plastics before putting them in recycling bins. Food waste and residues on recyclables can attract cockroaches.
- Restrict eating areas: Avoid eating outside of your kitchen or dining room to limit potential food spillage that could attract cockroaches in other areas of your home.
- Clean pet bowls: Empty your pet's water and food bowl regularly to prevent cockroaches from finding an easy meal.
- Maintenance of appliances: Deep clean your cooking appliances (stove, oven, refrigerator) daily, focusing on any narrowed gaps from grease and spilled food.
- Manage outdoor spaces: Protect your home's perimeter from bugs and other pests by ensuring there’s a 3-foot gap from plants and other foliage to your home's perimeter.
- Address Infestations: If your home is already infested, consider calling a pest control company to address the situation.
By incorporating these measures, you can help to make your home inhospitable to cockroaches and reduce the risk of an infestation. However, if a serious infestation occurs, it's recommended to contact a cockroach control specialist immediately.
Contact EcoGuard if You Are Dealing with Cockroaches
Cockroaches can be a daunting pest to deal with, but you're not alone in this battle. Here at EcoGuard Pest Management, we specialize in resolving infestations quickly, effectively, and with a dedication to environmentally friendly methods. Don't let the presence of cockroaches disrupt your peace of mind and the comfort of your home. Reach out to us today and let our team of professionals help you reclaim your space from these pesky invaders. Remember, a pest-free home is just a call or click away with EcoGuard Pest Management. Schedule your appointment now and let us help you towards a cleaner, safer, and cockroach-free home.
Cockroach Diet FAQs
-
What do roaches eat when there is no food?
When conventional food sources are unavailable, cockroaches have been known to feed on items like cardboard, paper, book bindings, leather, and even soap. Thanks to their digestive symbiosis with bacteria, they can extract nutrients from these unconventional sources.
-
What food attracts roaches best?
Roaches are particularly attracted to starchy and sugary foods, such as bread, cereal, sugar, and sweets. However, cockroaches are omnivorous scavengers and will consume a wide range of foods if necessary.
-
What are 10 things cockroaches eat?
Ten things that cockroaches eat include crumbs, grease, cheese, meat, pet food, baked goods, sweets, fruit, plants, and other insects. Remember that they can also consume unconventional items like cardboard and soap in the absence of other food sources.
-
What do cockroaches hate?
Cockroaches dislike certain smells and substances, such as those from citrus, mint, and eucalyptus. They also detest boric acid and diatomaceous earth, both of which are commonly used in pest control due to their lethal effects on roaches.
Request A Free Estimate
We will get back to you as soon as possible
Please try again later
Immediate Service Available
Services
Customer Care
Legal
Working hours
- Mon - Sun
- -
All Rights Reserved | EcoGuard Pest Management | All Phone Calls Recorded | By Using Website You Agree To Terms Of Use